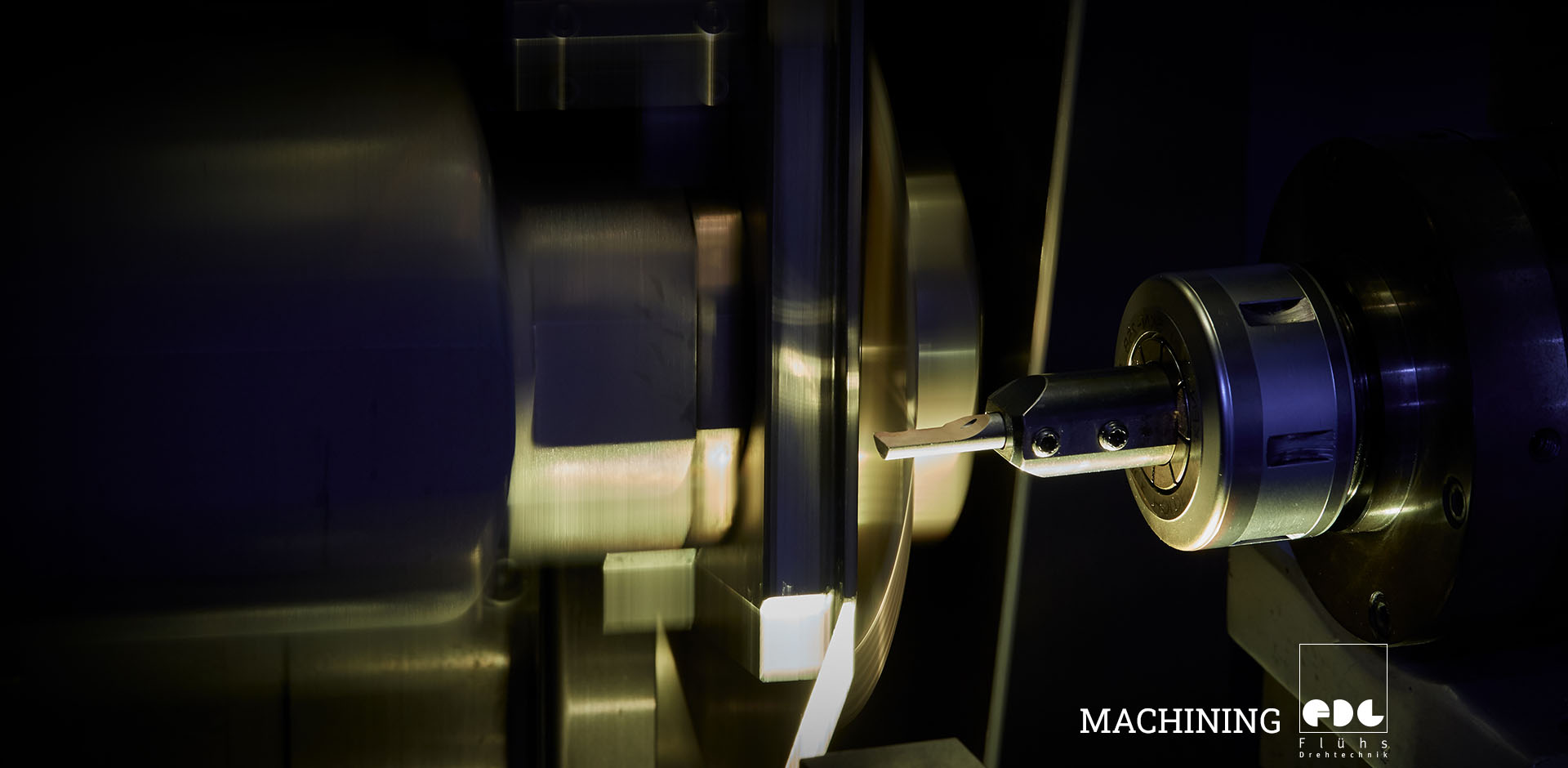
Machining (also known as cutting or chip removal) is a collective term for subtractive manufacturing processes in which workpieces are given a specific geometric shape by continuously removing material from their surface. An example of machining is the process of forming metal rods into screws.
According to DIN 8580 (the industry standard for manufacturing processes), machining belongs to the main group of separating processes. The 4 most important cutting processes are turning, milling, grinding, and drilling. In the metalworking industries, turning, drilling, and milling are particularly widespread.
In all machining processes, excess material (chips) is removed from a workpiece, for example, a metal bar. This makes the component smaller and changes its shape. There are 3 different types of chips that are formed during the machining process: continuous chips, discontinuous chips, and shear chips.
A continuous chip is formed in the shear zone by plastic deformation and is uniform in shape. It is produced at high cutting speeds and temperatures, with the cutting tool in continuous contact with the material.
Discontinuous chips or segmental chips are often generated when machining brittle materials. The chip breaks off in front of the cutting edge without significant deformation as a result of a tear. Discontinuous chips produce a rough surface and often occur when machining particularly brittle materials, such as ceramics, glass or hardened steel.
A shear chip is created by deformation in the shear zone and occurs in high-strength materials with low ductility, such as titanium. The material is stressed beyond its forming capacity and tears apart parallel to the shear plane.
Most ferrous and non-ferrous (NF) metals, such as aluminum, brass, red brass, or stainless steel, are suitable for machining. Wood and plastics can also be machined. Materials with very high strength, such as titanium, are difficult to machine; they require the use of special, very sharp-edged, and hard tools.
Machining can be carried out manually or automatically. In an industrial context, mechanical machining processes are generally used, inter alia, by machining centers, CNC machines, or similar.
There are different types of machining, which are explained below.