Material Preparation
First, grease and dirt must be removed from the turned part by brushing and using alkaline cleaners. This creates a clean, even surface that ensures uniform heat absorption during the annealing process.
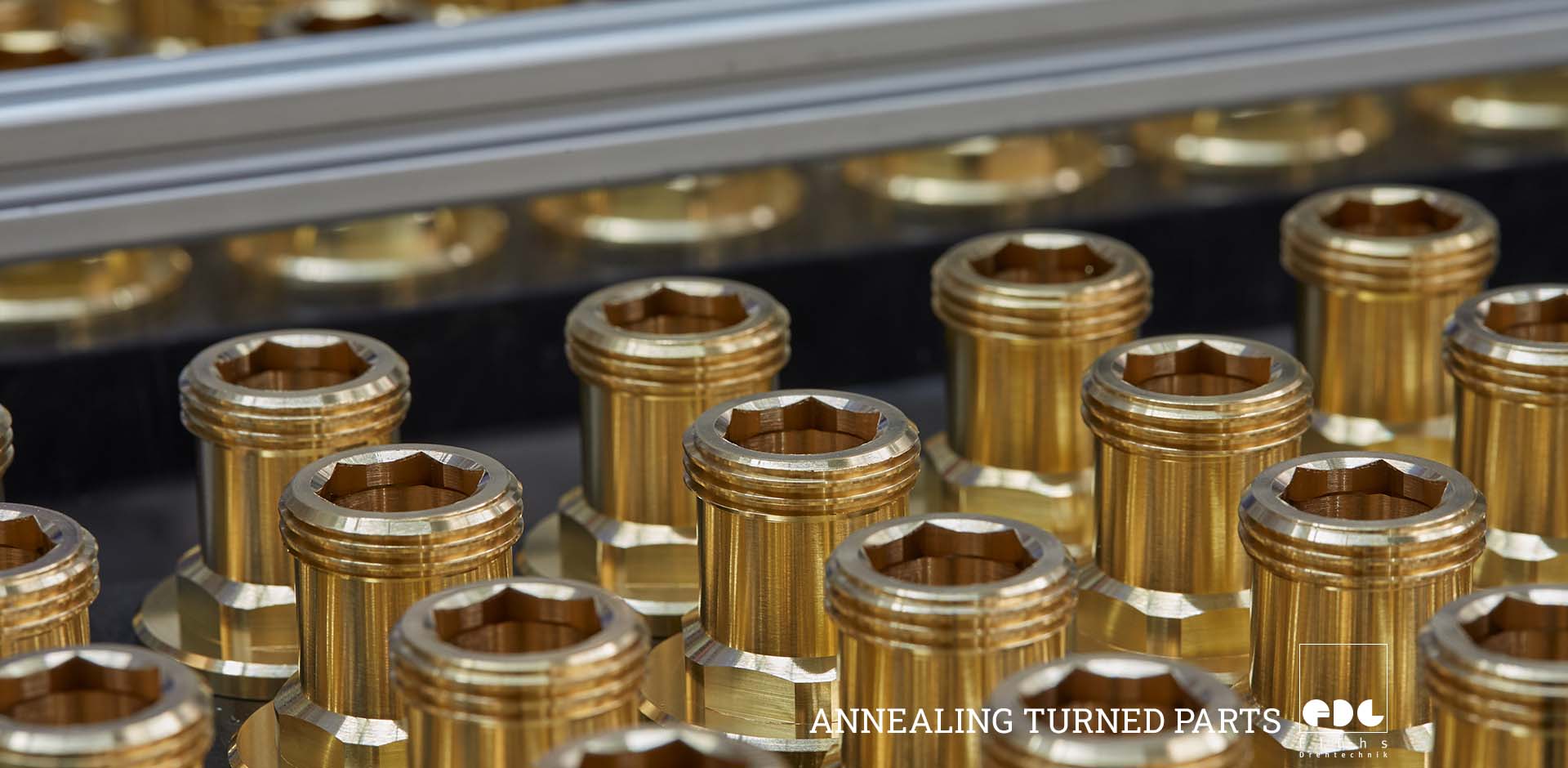

Annealing turned parts is one of the finishing processes offered by Flühs Drehtechnik. Annealing turned parts complements our extensive range of machining processes, which also includes electroplating, diamond turning and polishing. We work to the highest standards of quality management, based on DIN ISO 9001, VDA 6.1, and ISO TS 16949.
For detailed information about our services in the field of turned parts annealing, please contact us by email at info@fluehs.de or by phone at +49 2351 975-0.
Annealing is a heat treatment process that alters the physical properties of metal by heating and cooling it in a controlled manner. The aim is to improve the manufacturing properties of the metal, particularly with regard to machinability, formability, and mechanical strength.
Annealing is carried out in several defined steps: First, the material is prepared, then heated to a specific temperature. During the holding time, recrystallization takes place before the component is finally cooled in a controlled manner.
Annealing improves specific mechanical properties of the material. These include, in particular, increased ductility, improved machinability, and a more homogeneous structure. Depending on the material, intended use, and desired result, different annealing processes are used, such as soft annealing, stress relief annealing, or recrystallization annealing.
Annealing optimizes material properties and creates stable, resilient components that are easy and cost-effective to machine.
On this site, we describe the necessary processing steps for annealing turned parts and explain the purpose of annealing, the different types of annealing, and the advantages of annealing turned parts.
Annealing turned parts leads, among other things, to the improvement of various mechanical properties, which are described in the following section.
The purpose of annealing turned parts is to change the material properties of a metal for a specific aim. Annealing makes the material softer and more flexible, which increases its bendability and reduces its hardness. This reduces its susceptibility to breakage and improves the machinability of the workpieces.
Annealing turned parts achieves optimized properties for various metals. Steel, for example, benefits from stress relief and improved machinability. Annealing makes aluminum softer and more malleable. Annealing improves the ductility of copper and brass, making them easier to work with. At the same time, work hardening is reduced, which is particularly advantageous in multiple forming processes.
Annealing turned parts can be beneficial for the subsequent machining of the metal. Annealing softens the metal, which reduces tool wear. CNC machining of complex geometries often causes internal stresses in the material. Annealing effectively relieves these stresses, which not only reduces the risk of deformation or cracking, but also reduces the risk of stress corrosion cracking. The latter is caused by the interaction of tensile stresses in the workpiece and corrosive environmental conditions and can lead to unexpected failure, especially in high-strength materials.
Internal stresses often occur during CNC machining of complex turned parts. These are relieved by annealing, which prevents cracks and deformations.
Annealed turned parts can be easily formed due to their increased ductility, without the risk of breakage. Annealing turned parts thus contributes to their increased service life.
Depending on the annealing process selected, specific properties can be adjusted, for example through stress relief, soft annealing, or recrystallization annealing.

Turned parts are annealed by heating a metal to recrystallization temperature and then cooling it to improve its ductility, reduce its hardness, and relieve internal stresses. Annealing turned parts changes the internal metallic structure of the turned parts. The internal structure of the metal consists of so-called grains, which are individual crystalline areas. The most important factors influencing the end result of annealing are the heating temperature, the holding time, and the cooling rate. These parameters vary depending on the material and the desired annealing effect.
There are different types of annealing, which are described in the following section.
Soft annealing/GKZ annealing (spheroidizing)
oft annealing, often used synonymously with GKZ annealing or spheroidizing, is used to improve the formability and machinability of the metal in turned parts. GKZ annealing is used for steels with a carbon content of > 0.8%.
Recrystallization annealing/recovery annealing
Recrystallization annealing serves the purpose of fully or partially restoring the mechanical properties of a cold-formed workpiece. This is done in the temperature range between 300°C and 400°C.
Stress relief annealing
argeted heating and slow cooling reduce internal stresses without significantly altering the mechanical properties of the metal. This is particularly important in order to prevent stress corrosion cracking and distortion during further processing.
Normalizing/Normal annealing/grain refinement
Normal annealing serves to eliminate an inhomogeneous structure caused by casting, forging, or rolling. Annealing refines the grain structure, thereby improving the toughness and strength of the metal.
Diffusion annealing
When steels with high alloy concentrations solidify, the alloying elements may not be distributed homogeneously in the microstructure. Diffusion annealing compensates for these concentration differences.
Coarse grain annealing
Coarse grain annealing produces a coarser grain, which increases creep strength and improves the machinability of low-carbon steels.
Stabilization annealing
This process protects high-alloy, weldable steels from intergranular corrosion by controlling carbide precipitation. The temperature range for stabilization annealing is therefore between approximately 850°C and 1,050°C.
Solution annealing
Solution annealing improves the corrosion resistance of austenitic steels. The process involves heating the steel alloy until all the elements are in solution, allowing them to precipitate during subsequent precipitation annealing.
Depending on the material of the turned part, different annealing processes can be considered. This allows many different advantages to be achieved when annealing turned parts.
Annealing turned parts offers numerous advantages for the subsequent machining and use of the components. It optimizes mechanical properties such as formability and ductility while reducing unwanted internal stresses that arose during previous manufacturing steps, such as cold forming or welding.
Annealed turned parts feature an improved surface quality. The grain structure of the metal is refined by the annealing process, resulting in a more uniform and smoother surface.
A significant effect of annealing is an increase in ductility. The material becomes more ductile and thus less susceptible to stress corrosion cracking – a phenomenon caused by the interaction of tensile stresses and a corrosive environment. By reducing this risk, annealing contributes significantly to increasing the service life of turned parts.
The elimination of internal residual stresses in the metal is another advantage of annealing turned parts. Internal stresses caused, for example, by cold forming or welding are relieved by annealing.
In addition to the option of annealing the manufactured turned parts, Flühs already uses thermally relaxed raw material or bar stock in certain areas of application. The targeted selection of low-stress raw materials supports stable and deformation-free machining of the turned parts right from the start.
The annealing of turned parts is one of several complementary services offered by Flühs. Other surface finishing processes include polishing, electroplating, powder coating, and PVD coating. All processes are carried out in accordance with high quality standards and are tailored to the specific requirements of the respective application.
Please fill in the blanks below and send us your questions and requests.