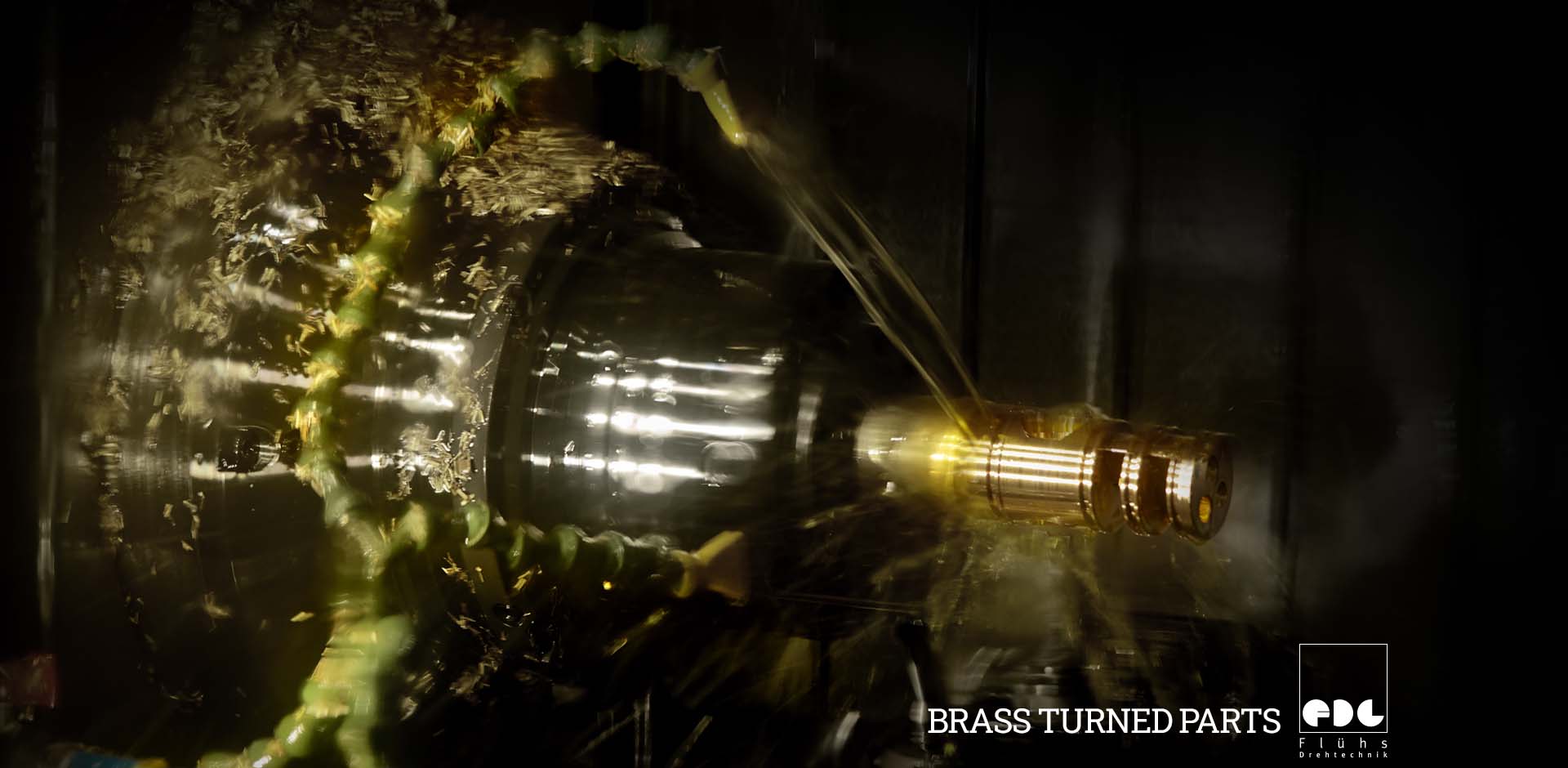
Brass Turned Parts from the Manufacturer:
Small, Medium & Large Series | Flühs
Brass turned parts manufactured by Flühs are available in small, medium, and large series.
Since 1926, Flühs has specialized in the versatile material brass and built outstanding expertise in manufacturing high‑quality brass turned parts.
For detailed information, please contact info@fluehs.de or call +49 2351 975-0.
Brass turned parts consist of an alloy of copper and zinc. The ratio between copper and zinc depends on the intended processing and use of the brass turned part.
Brass turned parts have different copper and zinc ratios depending on their intended use, although it is common to add other metals such as silicon or lead. The addition of other metals can improve machinability and certain physical properties such as corrosion resistance and strength.
Brass turned parts are manufactured using CNC automatic lathes or cam-controlled lathes in order to deliver a consistent level of quality. In this way, brass turned parts can be produced in small, medium and large series.
The following text deals with brass turned parts, the different types of brass turned parts and their advantages and disadvantages. It also explains which brass turned parts Flühs manufactures and how the manufacturing process works.
Brass Turned Parts
Brass turned parts are components made from a copper‑zinc alloy that are produced with special turning tools. They are used, for example, as screws, latches, valves, and more across industrial and household applications.
Depending on the copper‑to‑zinc (Cu‑Zn) ratio, we distinguish alpha and beta brass.
Alpha brass forms at a zinc content of up to 35%, the remainder being copper. It offers excellent corrosion resistance, very good cold formability, and an attractive polished sheen.
Beta brass forms at greater than 35% zinc. Up to about 34% zinc, alpha and beta phases can occur in combination; above 35%, only beta brass remains. Beta brass has high wear resistance and can be strengthened by heat treatment. Because of its relatively low melting point, it is often used in die casting. For both alpha and alpha‑beta brasses, other elements such as lead, silicon, nickel, or aluminum can be added for specific properties.
Brass with more than 45% zinc is typically not relevant for technical applications.
What types of brass turned parts exist?
There are different types of brass turned parts, the alloy composition of which varies depending on the required properties such as corrosion resistance, hardness or electrical conductivity.
In an industrial context, brass turned parts often consist of the alloys copper-zinc, copper-zinc-silicon and copper-zinc-lead.
-
Brass turned parts made from Cu‑Zn alloy (CuZn42)
CuZn42 (approx. 58% Cu / 42% Zn) continues to gain market share because it is lead‑free.
-
Brass turned parts made from Cu‑Zn‑Si alloy (CuZn21Si3P, “lead‑free free‑machining brass”)
Typically 75-77% Cu, 21% Zn, 3% Si. This material offers increased strength and hardness, very good corrosion behavior, and is excellent for electroplated finishes. CuZn21Si3P is approved for potable‑water applications and is therefore widely used in the plumbing industry.
-
Brass turned parts made from Cu‑Zn‑Pb alloy (CuZn40Pb2, “free‑machining brass”)
Typically 57-59% Cu, 38-40% Zn, 2% Pb. Also known as free‑machining brass because it is widespread in CNC production and well suited to hot forming. It is excellent for electroplated finishes. CuZn40Pb2 is approved for potable‑water applications and is therefore frequently used in the plumbing industry, particularly for valves. Increasing regulatory restrictions in many parts of the world have already reduced and will significantly further reduce the usage of leaded brass alloys.
Which brass turned parts does Flühs manufacture?
Flühs produces brass turned parts from Cu‑Zn alloys with and without lead, as well as special brasses containing silicon, for example.
Alloy selection depends on the intended use of the part. For potable‑water contact, lead content is limited in both the U.S. and Europe. Flühs copper alloys already comply with RoHS and REACH regulations.
Some of the most important copper-zinc alloys used by Flühs in production are described below.
CW617N, also known as MS58, is a copper-zinc alloy with a lead content of ≤ 2.2%. This alloy is easy to machine and form, which is why it is often used in precision mechanics and, until now, in drinking water applications.
CW510L or CuZn42 is a lead-free copper-zinc alloy with a copper content of 57-59%. This alloy is suitable for drinking water and is therefore used by us to manufacture turned parts or valves for sanitary fittings.
CW724R is a special brass with silicon, which is particularly suitable for sanitary applications due to its good corrosion resistance. The copper content is 75-77 %, the silicon content 2.7-3.5 % and the zinc content approx. 21 %. The addition of silicon improves resistance to stress corrosion cracking and dezincification.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of brass turned parts?
The main advantages of brass turned parts are their attractive physical and hygienic properties and their recyclability. One of the few disadvantages of brass turned parts is the comparatively high purchasing costs.
The positive physical properties of brass turned parts include, above all, the low coefficient of friction and high corrosion resistance. Brass develops a protective oxide layer that makes it more resistant to corrosion.
The antimicrobial properties of brass make it a safe material for sanitary systems. The surface of the brass swivel part prevents the spread of bacteria and germs. Brass turned parts are 100% recyclable. According to an estimate from the World Copper Factbook 2024 by the International Copper Study Group, 32% of the copper used worldwide is already recycled copper.
The main disadvantage of brass turned parts is that they are more expensive to purchase than other common metals such as aluminum or stainless steel. The mechanical processing of brass is comparatively easy, which is why brass is cheaper in terms of workability than stainless steel, for example. Brass is also a fairly heavy metal, which can make it difficult to handle. Another disadvantage of brass is its sensitivity to acidic solutions and chemicals (such as ammonia), which can lead to stress corrosion cracking in brass if exposed to them for long periods.
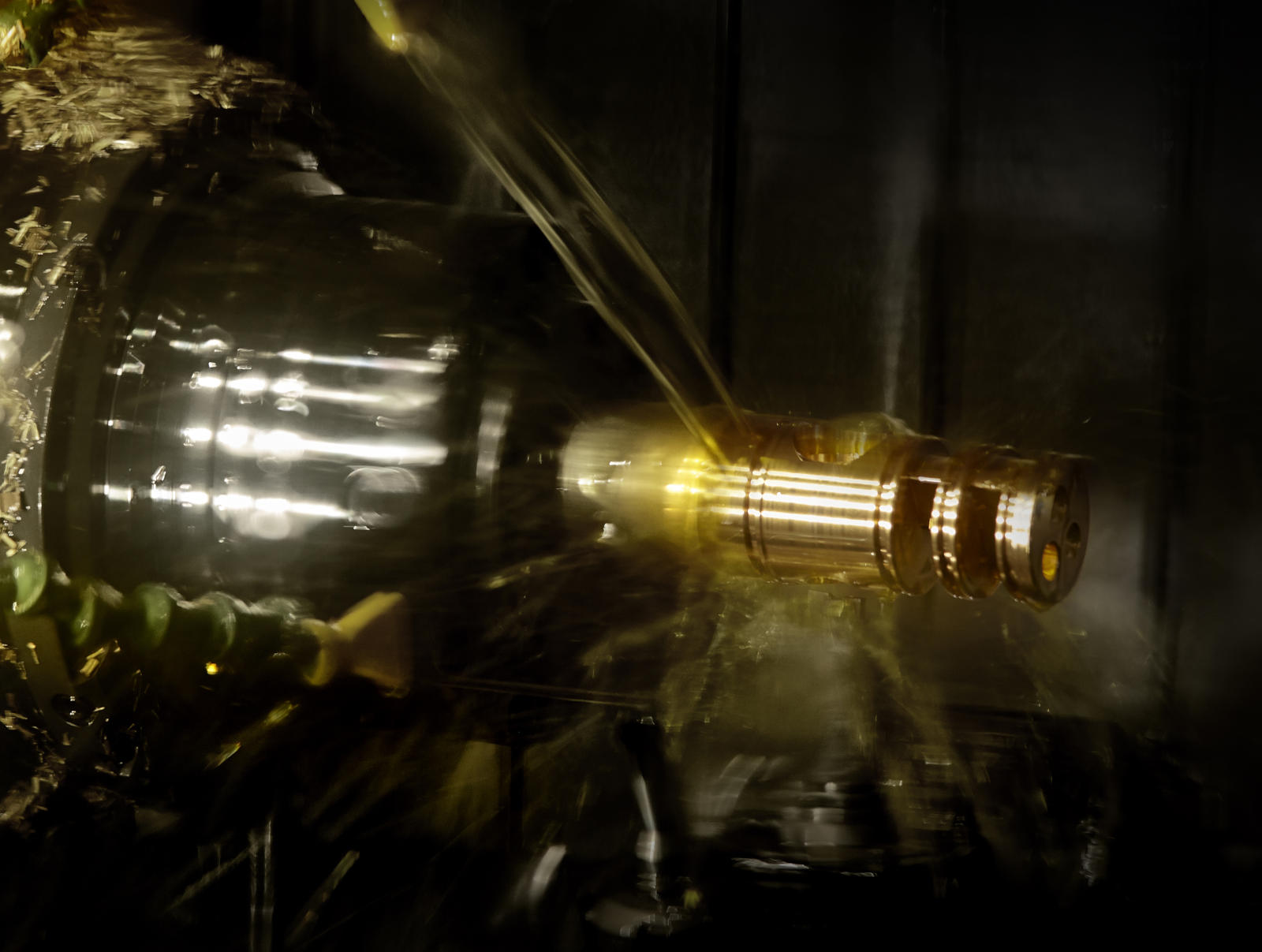

How are brass turned parts manufactured?
Brass turned parts are manufactured by shaping a workpiece with special tools on CNC turning lathes or cam‑controlled lathes. While the workpiece rotates, the drilling, milling, cutting, and form tools remove material to achieve the desired geometry.
The automation of the manufacturing process with lathes and automatic lathes ensures increased precision and quality of the brass turned parts. At the beginning, the workpiece is automatically loaded onto the lathe. The turning process then starts, in which the workpiece is shaped into the desired form by cutting tools removing material during turning. This is followed by further processing with forming tools to achieve the required accuracy in shape and surface.
If necessary, after turning and removing the finished brass turned part, the surface is finished by electroplating, polishing or coating.
Thanks to its versatile and modern machinery, Flühs is able to produce individual brass turned parts in small, medium and large series.
Customized Brass Turned Parts in Small, Medium, and Large series
Flühs manufactures individual brass turned parts in small, medium and large series.
We use mechanical and computer-controlled single and multi-spindle automatic lathes for the production of brass turned parts. We always use CNC automatic lathes for the production of long turned parts. Complicated turned parts are produced on flexible turn-mill centers in a single machining process.
The series production of brass turned parts is carried out using CNC automatic lathes. During the production process, an accompanying quality control takes place, in which the quality assurance team checks tolerances and dimensions. The final inspection is fully automated with image processing machines, whereby bad parts are sorted out.
We source the brass rods, tubes and profiles we use exclusively from semi-finished product factories that supply first-class quality.
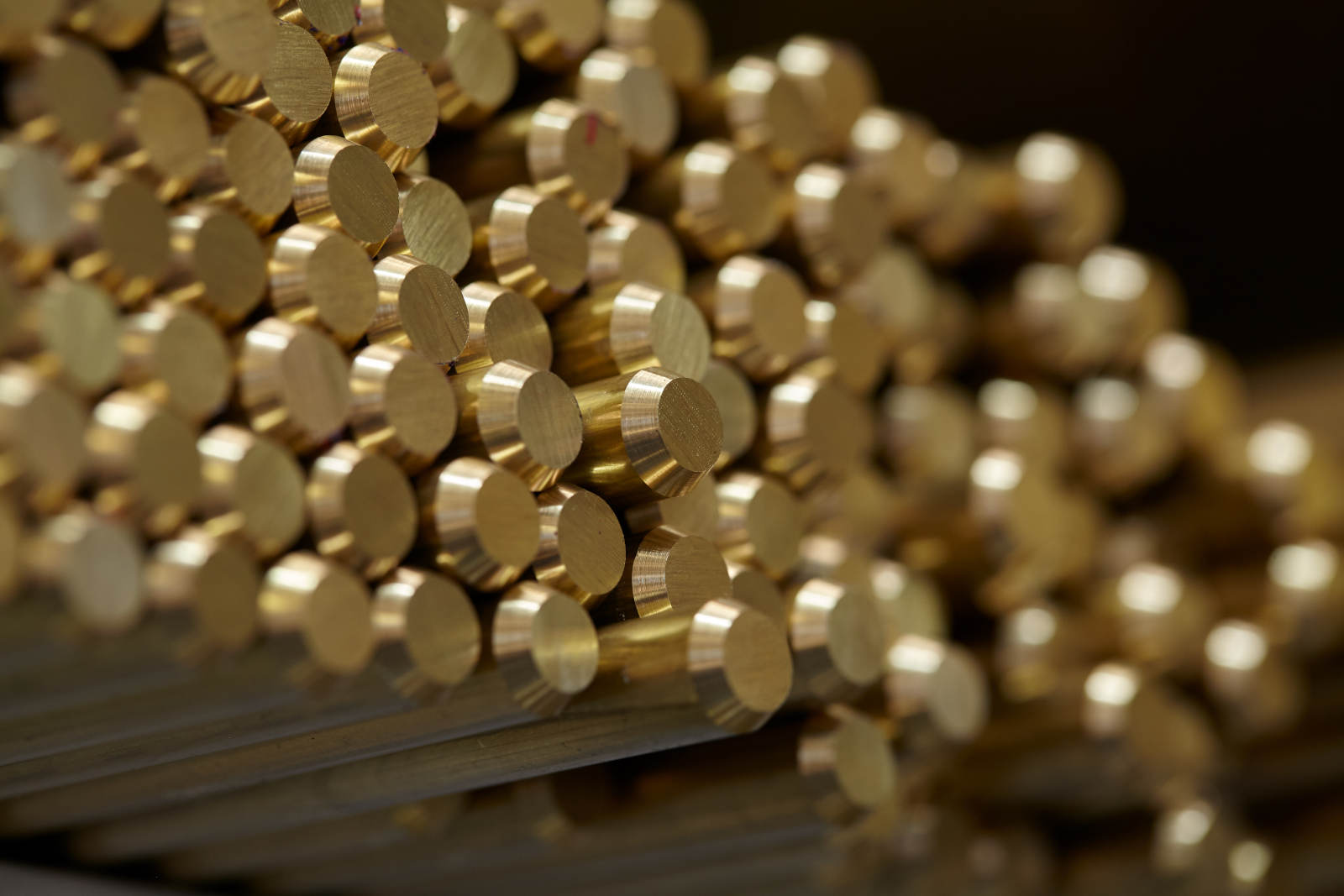


About us
Brass provides a durable foundation for many of our products. With 100 years of experience in brass turned parts, we deliver the level of quality that customers worldwide value. The Flühs team is happy to advise you on global certification requirements to help you make the right material choices for your product.
Our formula for success remains unchanged: high‑grade materials, precise state‑of‑the‑art manufacturing processes, and an in‑house quality‑management system based on ISO 9001 and ISO 14001. Over 200 patents are the result of our power to innovate, which has been with us for around a century.